💊 Oral Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors (CAI) for Glaucoma
Oral CAIs reduce intraocular pressure by suppressing aqueous production.
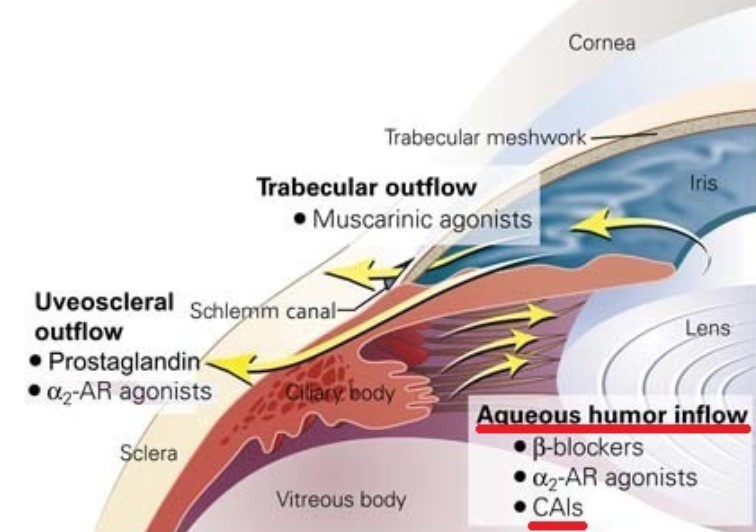
Used when topical therapy is insufficient or urgent pressure lowering is needed.

🧪 Comparison Table
ItemAcetazolamideMethazolamide
| Dose | 250mg up to 4/day | 50mg twice/day |
| Half-life | 4 hours | 12–15 hours |
| Excretion | Renal | Hepatic |
| Protein Binding | 95% | 55% |
| Strengths | Strong effect, IV available | Less systemic absorption |
| Limitations | Contraindicated in pregnancy, kidney caution | ⚠️ Risk of SJS |
✅ Mnemonics:
- “High PPK” → Protein, Potency, Kidney = Acetazolamide
- “Low Systemic, Long Half-life” → Methazolamide
⚠ Key Side Effects
EffectNotes
| Paresthesia, anorexia | Due to ↓K+, advise orange juice intake |
| Metabolic acidosis | HCO₃- loss → avoid in DM, COPD, liver issues |
| Hematologic toxicity | WBC↓, PLT↓, pancytopenia |
| Kidney stones | Rare in low doses, but possible in high-dose |
| SJS (Stevens-Johnson) | Rare but severe, mainly with methazolamide |
✅ Summary
- Oral CAIs are powerful IOP-lowering agents,
- but require caution due to systemic side effects, especially SJS




Comments