Tistoryview
Disease&Treatment/Retina
Coats' disease, Coats' disease causes treatment symptoms tests prognosis blindness
eye_doc 2025. 4. 21. 20:28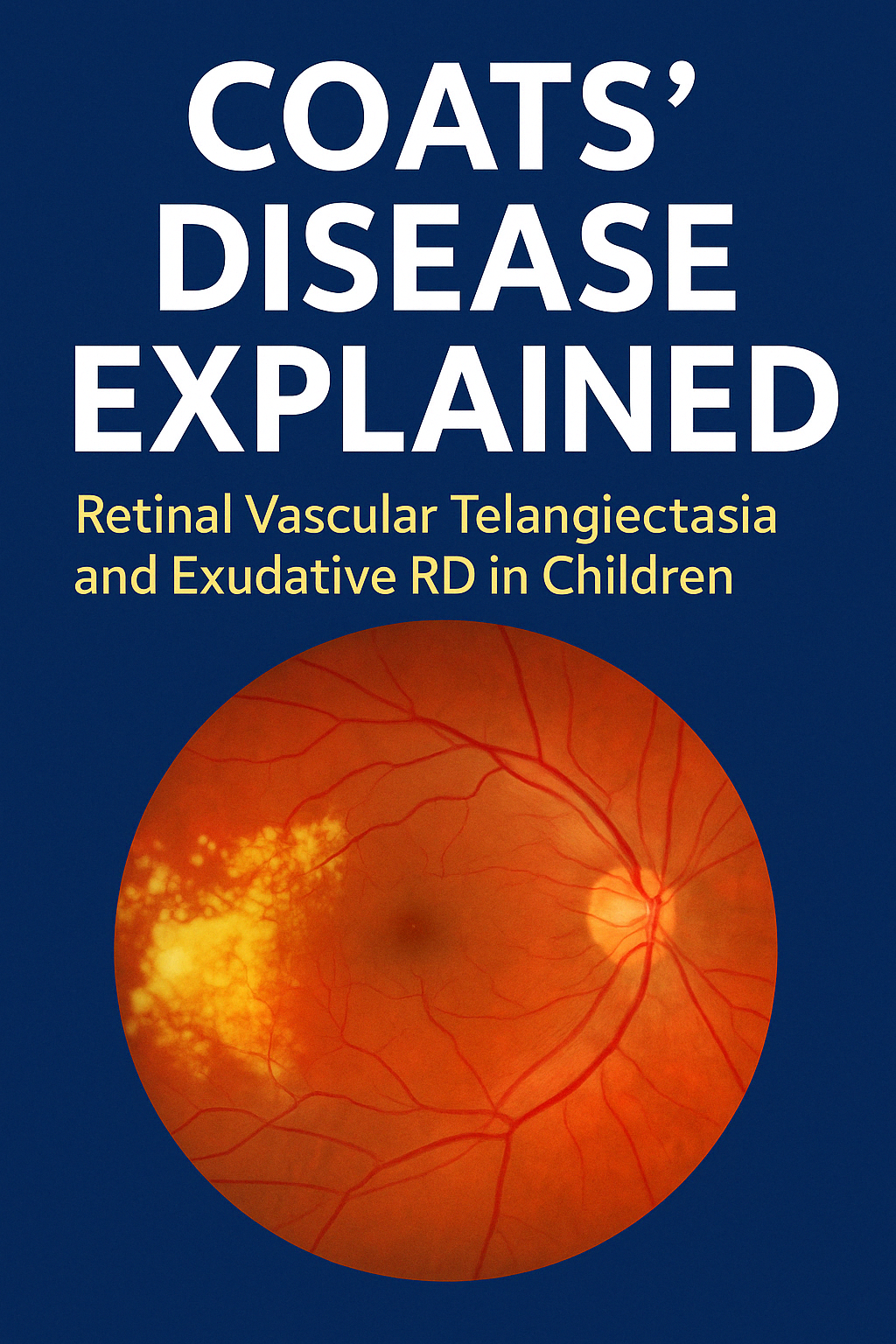
👁 Coats' Disease – A Progressive Pediatric Retinal Vascular Disorder
Coats' disease is a rare, typically unilateral pediatric retinal disorder
characterized by retinal telangiectasia, lipid exudation, and exudative retinal detachment.
It most commonly presents in young boys (<10 years) and may lead to vision loss or enucleation.
✅ Clinical Summary
FeatureDescription
| Onset | Mean age ~5 years, 75% male |
| Eye Involvement | Unilateral in 95% |
| Symptoms | Decreased vision, leukocoria, strabismus |
| Fundus | Telangiectatic vessels, yellow-white exudates |
| Complication | Total RD, NVG, Phthisis |
| Cause | Idiopathic, possible NDP gene mutation |
| Diagnostic Tools | Fundoscopy, FAG, OCT |
✅ Treatment Overview
StageTreatment
| Early | Observation, laser photocoagulation |
| Moderate | Cryotherapy, anti-VEGF |
| Advanced | PPV, retinal detachment drainage |
| With NVG | Management of glaucoma |
| End-stage | Enucleation in phthisis |
