Tistoryview
Disease&Treatment/Glaucoma
Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome (PEX)? glaucoma, pupil cataract, true foliation
eye_doc 2025. 4. 20. 02:44👁 What is Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome (PEX)?
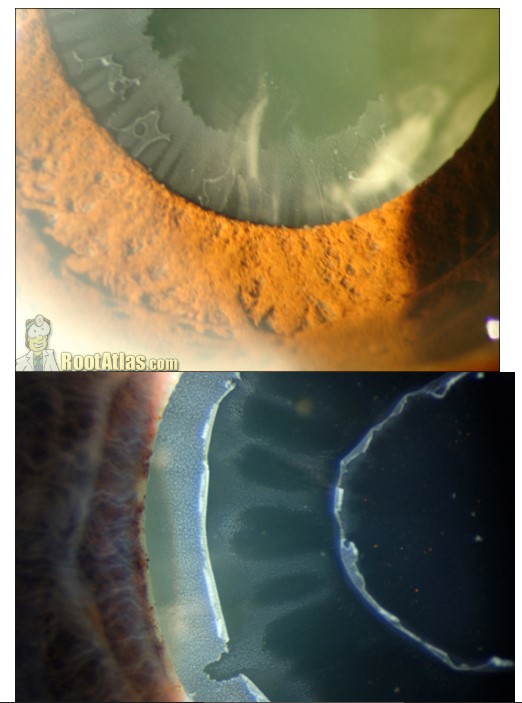
- PEX is a systemic ocular condition in which abnormal fibrillar protein deposits accumulate on the lens, iris, cornea, and other ocular structures
- First described by Lindberg in 1917
- Best observed after pupillary dilation
- Predominantly affects elderly patients, more common in females
🔍 True vs Pseudo Exfoliation
TypeDescription
| True exfoliation | Capsular delamination after infrared exposure |
| Pseudoexfoliation | Protein debris accumulation on intraocular surfaces |
📌 Clinical Significance of PEX
1. Increased Risk During Cataract Surgery
FindingRisk
| Poor pupil dilation | Difficult surgical visualization |
| Weak zonules | Risk of lens subluxation |
| Thin posterior capsule | Higher risk of rupture (PCR) |
| ➡️ Complication risk up to 5× higher |

2. Glaucoma Association
FactorNote
| Glaucoma risk ↑ | 10× higher than general population |
| Accounts for | 20–25% of open-angle glaucoma |
| IOP pattern | Higher, more fluctuation |
| Pathogenesis | PEX material blocks aqueous outflow |
➡️ PEX glaucoma is more aggressive and harder to treat
✅ Summary
- PEX is a serious condition beyond “debris” — it increases risks in cataract surgery and glaucoma
- Requires pupillary dilation for diagnosis
- Needs close monitoring, especially in older adults with poor dilation or suspicious ocular findings
