Tistoryview
Disease&Treatment/Glaucoma
Glaucomatous Optic Disc Cupping, damage of Retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) & Optic nerve fibers (axons)
eye_doc 2025. 4. 20. 01:44👁 What is Glaucoma?
Glaucoma is a progressive optic neuropathy
with structural and functional damage involving:
- Retinal ganglion cells (RGCs)
- Optic nerve fibers (axons)
✅ Diagnosis requires BOTH:
- Structural change (e.g. optic disc cupping)
- Functional loss (e.g. visual field defects)
💡 Analogy to Systemic Hypertension
Systemic HypertensionOcular Hypertension (Glaucoma)
| Narrowed vessels → high BP | Blocked outflow → increased IOP |
| Heart under strain | Optic nerve under pressure |
💧 Aqueous Humor & IOP Dynamics
- Produced in the ciliary body
- Flows: Posterior chamber → pupil → Anterior chamber
- Exits via trabecular meshwork (TM) and Schlemm’s canal
✅ Normal flow = stable IOP (10–21 mmHg)
❌ Blocked outflow = pressure buildup = IOP elevation

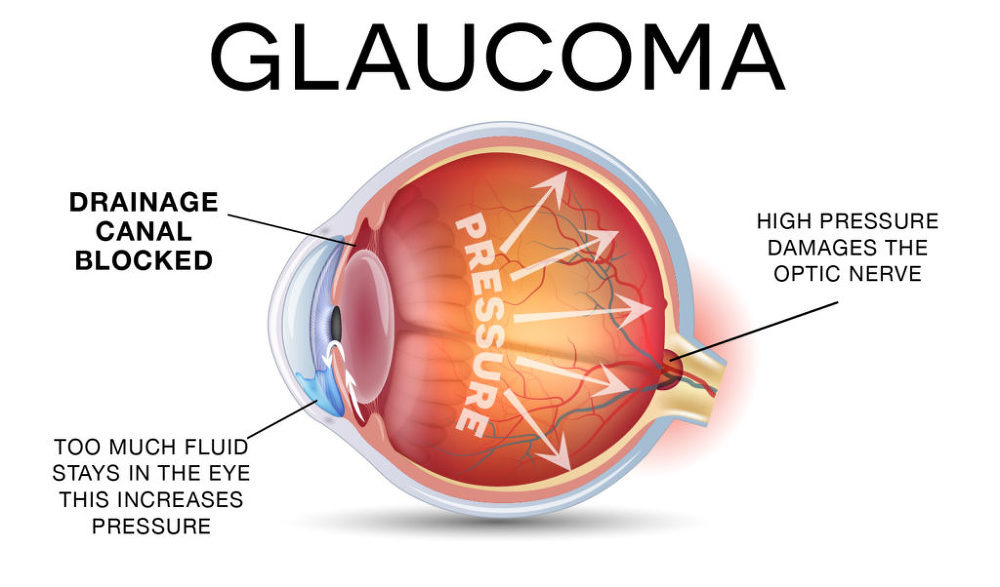
⚠ Pressure Targets the Optic Disc
- Optic disc = most vulnerable spot in the posterior eye
- High IOP causes focal inward depression (cupping)
- Normal cupping: small & symmetrical
- Glaucomatous cupping: larger, deeper, often asymmetric
📸 Features of Glaucomatous Optic Disc Cupping
FeatureNormal DiscGlaucomatous Disc
| Cupping size | Small | Enlarged |
| Rim appearance | Even | Notched/thinned |
| Blood vessels | Cross center | Shifted peripherally |
| Symmetry | Bilateral equal | Often asymmetric |
✅ Summary
- Glaucoma = IOP-induced optic nerve damage
- Optic disc cupping is the hallmark of structural change
- Functional loss confirmed via visual field testing
- Must monitor both structure & function for proper diagnosis
