Tistoryview
Disease&Treatment/Cornea&Ocular surfaces
Posterior Polymorphous Corneal Dystrophy (PPMD/PPCD) symptom, treatment, prognosis
eye_doc 2025. 4. 15. 19:54👁 What is Posterior Polymorphous Corneal Dystrophy (PPMD/PPCD)?
Posterior Polymorphous Corneal Dystrophy (PPMD/PPCD) is a rare, autosomal dominant
corneal dystrophy in which corneal endothelial cells take on epithelial-like characteristics.
🔍 Key Features
- Usually asymptomatic, no significant pain or vision loss
- Does not typically progress to stromal edema or severe corneal haze
- In rare cases, it may be associated with secondary glaucoma

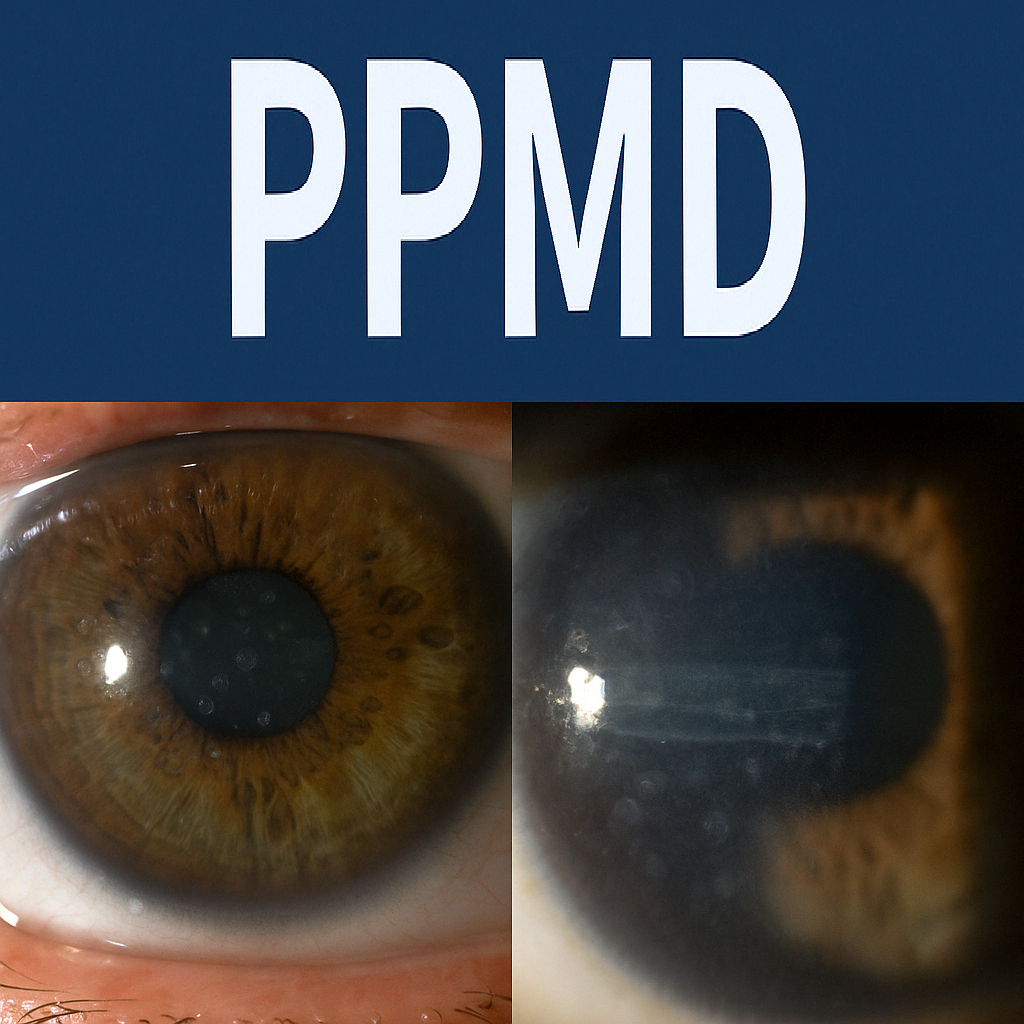
👁🗨 Corneal Appearance – 3 Variants
- Vesicle Type
- Small, round, well-defined lesions
- Resemble dark dots surrounded by healthy endothelium
- Band Type
- Merged vesicles forming wavy horizontal lines
- Run parallel but never intersect
- Diffuse Opacity Type
- Rare, more severe form with stromal edema and decreased vision
- May require corneal transplant
🧬 Pathology and Complications
- Abnormal endothelial cells may migrate toward the iris via trabecular meshwork
- Can lead to iris changes and secondary glaucoma
- Endothelial cell density generally remains above 500–1000 cells/mm²
💊 Treatment
- Observation only in most cases
- Hyperosmotic agents (e.g., Muro 128) used for early edema
- In advanced cases: corneal transplant may be considered
→ However, surgical outcomes are poorer if glaucoma is present
✅ Summary
- Rare inherited corneal dystrophy, usually non-progressive and asymptomatic
- Three clinical patterns: vesicle, band, and diffuse
- Monitor for glaucoma and visual deterioration
- Early diagnosis and careful follow-up are essential
